Drug Discovery
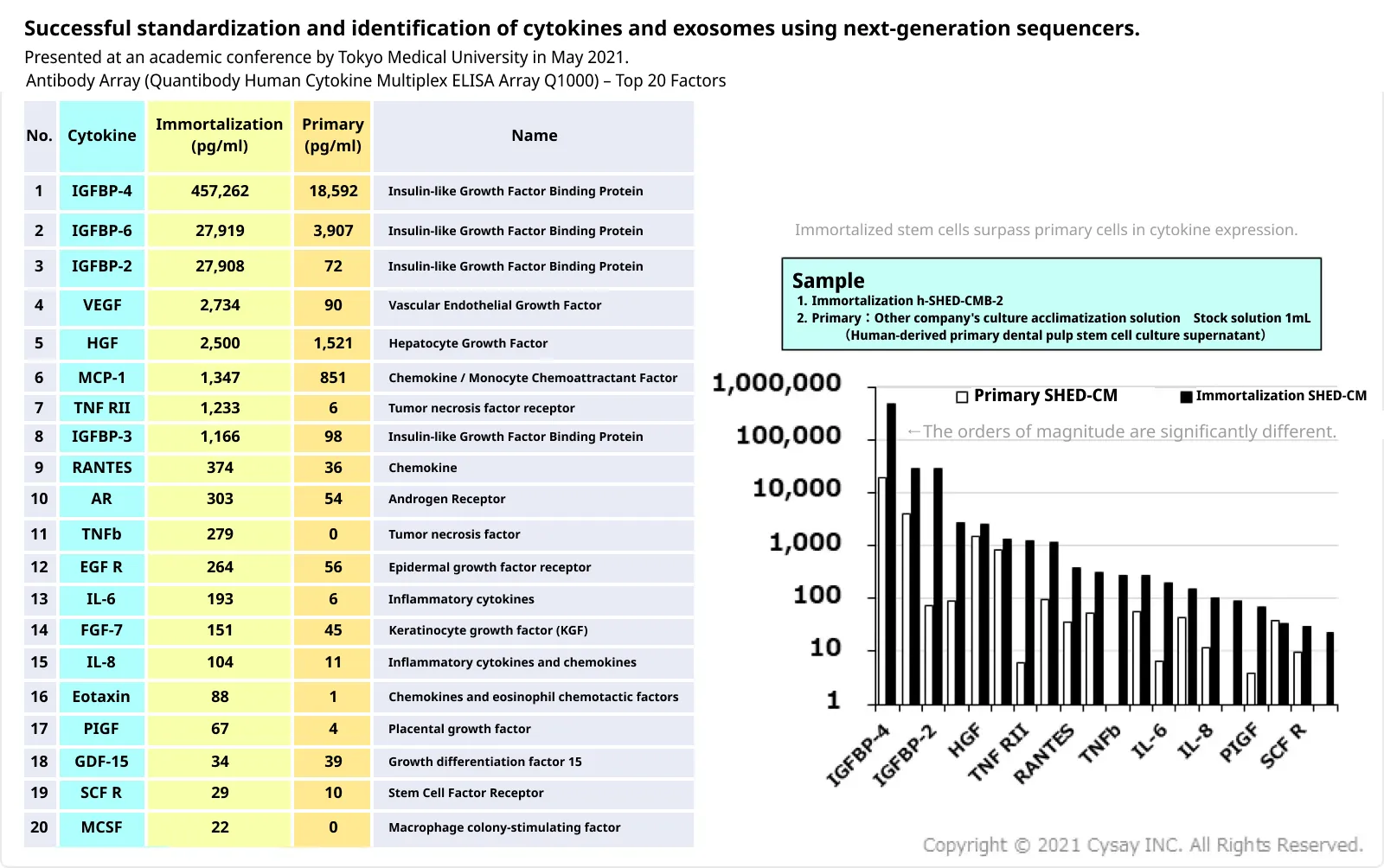
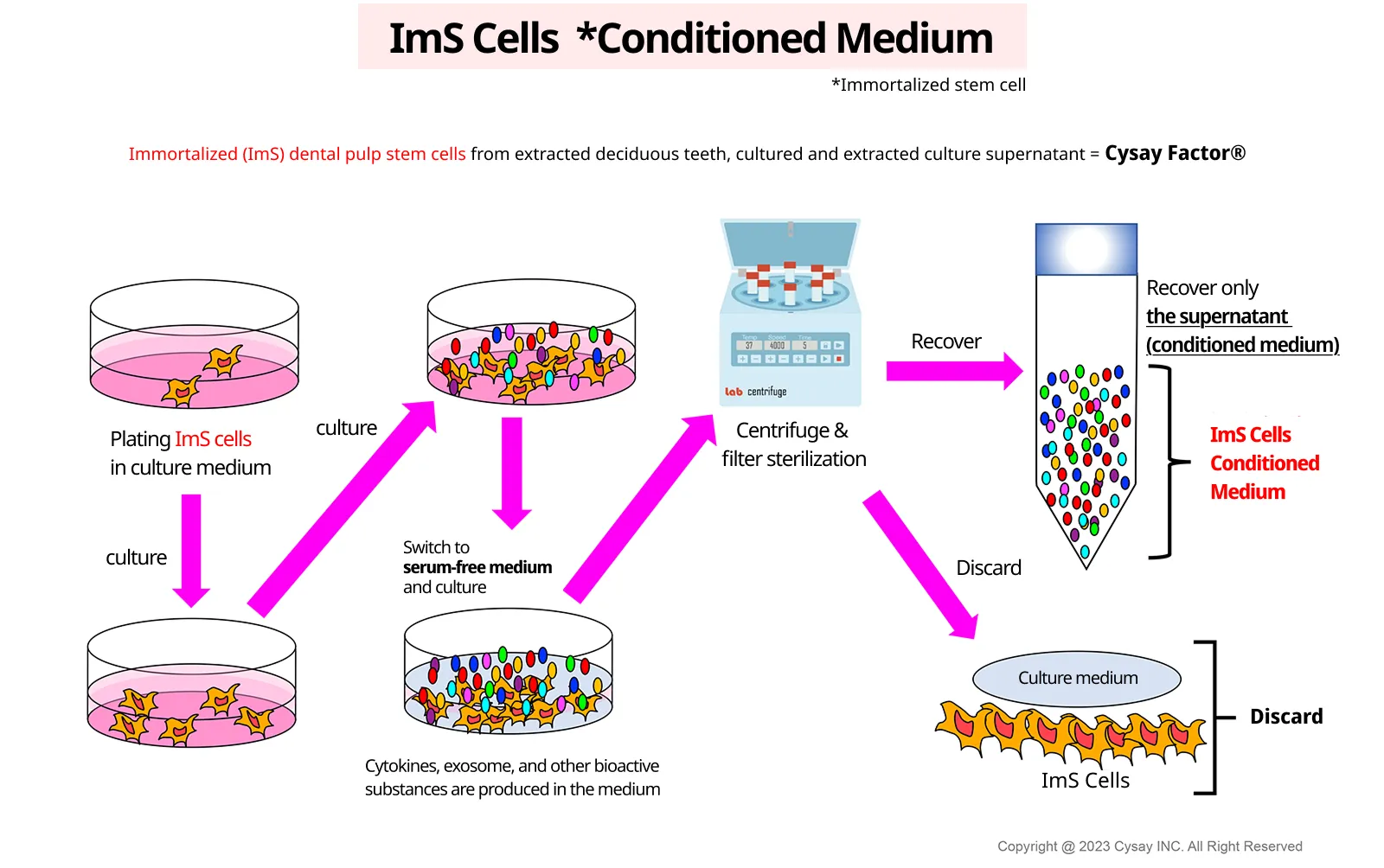
“Cysay Factor®” is the name of a cytokine mixture, a bioactive substance produced by stem cells, developed by our company in 2012 and named ‘Cysay Factor ®’ to differentiate it from conventional single growth factor extracts and other companies' products.
In order to eliminate genetic differences among donors and variations in the growth factors produced, we have immortalized the stem cells to maintain traceability and homogeneous quality control of the growth factors.
We are conducting drug discovery research and development to apply the regenerative and restorative capabilities of this immortalized dental pulp stem cell culture supernatant to pharmaceutical applications.


Publication
-
Date
Paper Title
-
January 13, 2023
Protective effects of conditioned media of immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth on pressure ulcer formation.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36713359/
Conference Presentations
-
Date Location
Paper Title
Conference Title -
October 20-23, 2024 Seoul, Korea
Therapeutic effect of conditioned medium from immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth against peripheral nerve injury through upregulation of Netrin-1 in a mouse model of sciatic nerve crush injury.
Cytokines 2024 and KAI2024, -
February 25-26, 2024 Sapporo, Hokkaido
Protective effect of conditioned medium of immortalized human exfoliated deciduous teeth against peripheral nerve injury in a sciatic nerve crush mouse model.
The 1st Annual Meeting of the Japanese Cytokine Society -
March 21-23, 2024 Niigata, Japan
Inhibition of Peripheral Neuropathy in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mouse Model by Secretome of Human Deciduous Dental Pulp Stem Cells
The 23rd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine -
March 21-23, 2024 Niigata, Japan
X-irradiation-induced protection of human deciduous dental pulp stem cell-derived acclimation medium against protective effect against graying.
The 23rd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine -
January 17-19, 2024 Chiba, Japan
Inhibition of melanogenesis by conditioned medium of an immortalized stem cell line from human exfoliated deciduous teeth through possibly Wnt5a-mediated suppression of Wnt signaling.
The 52nd Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Immunology -
May 25-26, 2023 Wakayama, Japan
Conditioned medium of immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth inhibit melanogenesis by suppressing Wnt signaling via Wnt5a.
JSICR/MMCB 2023 Joint Symposium. -
December 7-9, 2022 Kumamoto, Japan
SConditioned medium of immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth exhibit protective effect on the peripheral neuropathy of experimental autoimmune neuritis.
The 51st Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Immunology -
June 9-10, 2022 Tokyo, Japan
Protective effect of conditioned medium of immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth on the peripheral neuropathy of experimental autoimmune neuritis.
JSICR MMCB 2022 Joint Symposium -
March 17-19, 2022 Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan
Therapeutic Effects of Immortalized Human Shedding Deciduous Dental Pulp Stem Cell (SHED-CM) Culture Supernatant on Skin Ulcers in Decubitus Ulcer Model Mice
The 21st Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Regenerative Medicine -
December 8-10, 2021 Nara, Japan
Protective effect of conditioned media of immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth on the formation of acute pressure ulcers via HGF and VEGF.
The 50th Annual General Meeting of the Japanese Society for Immunology -
May 21-22, 2021 online
Therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of action of immortalized human gingival medulla-derived mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) culture supernatant on skin ulcers in a mouse model of decubitus ulcer
The 85th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research